IMS核心元素
对于IMS架构
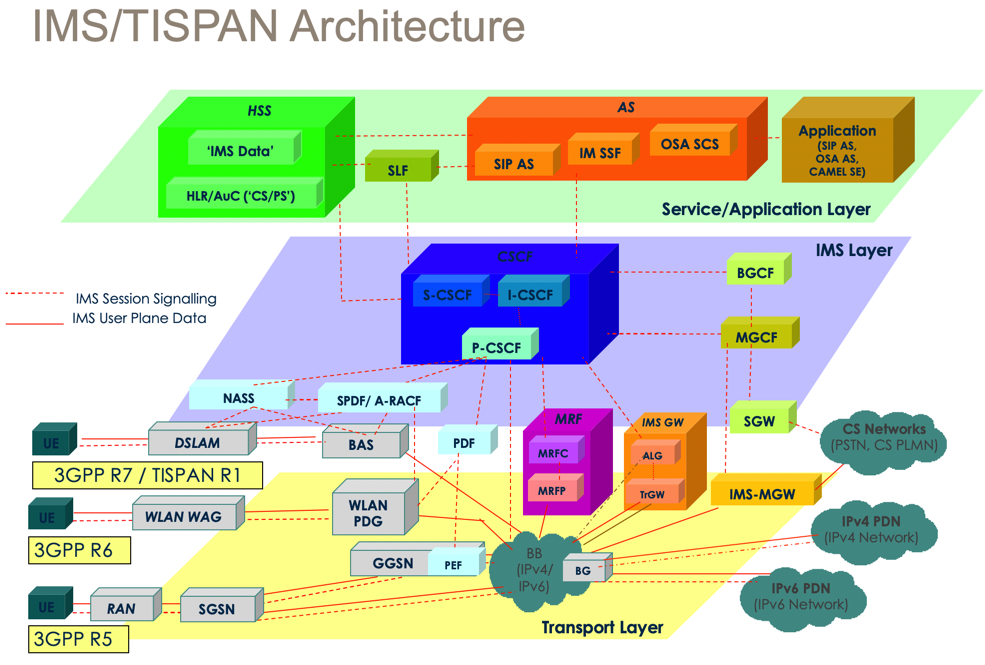
其中的:
- 核心元素和简介
AS=Application Server=应用服务器- Executes service logic associated with value-added services
- Provides enhanced and intelligent services to subscribers
CSCF=Call Session Control Function=调用会话控制功能P-CSCF=Proxy CSCF- is the first point of contact and the control point for the User Equipment (UE) within the Service Provider network. It forwards session requests from the UE to the S-CSCF
S-CSCF=Serving CSCF- has access to the user subscription data and actually handles the session request
I-CSCF=Interrogating CSCF- is the first contact point within a Service Provider network for all incoming session requests from another Service Provider
BGCF=Breakout Gateway Control Function- Identifies the network that will be used for connecting IP sessions to the PSTN
HSS=Home Subscriber Server=归属用户服务器=HSS用户数据库- Stores all the static and dynamic information for a subscriber
- Maintains a list of features and services associated with a user, and also the location and means of access to the user
- Provides user profile information
SLF=Subscription Locator Function- Queried during Registration and Session Setup to get the name of the HSS containing the required subscriber specific data
MGCF=Media Gateway Control Function- Controls the parts of the call state that pertain to connection control for media channels in a T-MGF MGW
- Selects the CSCF depending on the routing number for incoming calls from legacy networks
- Performs protocol conversion between ISUP and call control protocols (e.g., SIP) and maintains call states
MRFMRFC=Multimedia Resource Function Controller- Controls the media stream resources in the MRFP under direction from an S-CSCF or Application Server
- Interprets information coming from an AS or S-CSCF (e.g., session identifier) and controls MRFP accordingly
MRFP=Multimedia Resource Function Processor- Provides media resources under the direction of MRFC
- May generate media streams (e.g., multimedia announcements), mix incoming media streams for multiple parties, or process media streams (e.g., audio trans-coding, media analysis)
PDF=Policy Decision Function- Provides management of network QoS resources, authorization of resource allocations, and makes policy decisions with regard to use of network QoS resources
SPDF=Service Policy Decision Function
T-MGF=Trunk Media Gateway Function- Terminates bearer channels from a switched circuit network and media streams from a packet network (e.g., RTP streams in an IP network)
- Establishes and releases connections between these channels under control of the MGCF in support of calls between PSTN and IP network
SGF=Signaling Gateway Function- Acts as a gateway between the IP call/session control signaling and the SS7-based PSTN signaling
- May provide signaling translation, for example between SIP and SS7 or simply signaling transport conversion e.g., SS7 over IP to SS7 over TDM
A-BGF=Access Border Gateway Function- Packet gateway between an access network and a core network used to mask a service provider’s network from access networks, through which UE accessing packet-based services (e.g., IMS, Internet)
- Functions may include Opening and closing gate, Traffic classification and marking, Traffic policing and shaping, Network address and port translation, and Usage information
- Under control of the PDF
I-BGF=Interconnection Border Gateway Function- Packet gateway used to interconnect a service provider’s core network with another service provider’s core network supporting the packet-based services
- Functions may be the same as that of the A-BGF
I-BCF=Interconnection Border Control Function- Controls I-BGF to interwork with other packet-based networks
- May support the following functions (not limited to)
- Inter-domain protocol normalization and/or repair
- Inter-domain protocol interworking
- Interaction with PDF for resource reservation, resource allocation, and/or other resource related information
MRB=Media Resource Broker- Assigns specific media server resources to incoming calls at the request of service applications (i.e., an AS)
- Acquires knowledge of media server resources utilization and reservation requests that it can use to help decide which media server resources to assign to resource requests from applications
- Employs methods/algorithms to determine media server resource assignment